The human bones have a flexibility level that creates it capable of resisting forces applied thereto. However, once a powerful force that exceeds the resistance level of the bone is applied, the bone absorbs the shock causing it to break or fragment. Bone fractures are classified into two main types namely, the non-displaced and the displaced fractures.
Most of the time non-displaced fractures are considered mild cases because even bones are fractured, the fragmented pieces still remained on their proper alignments. Displaced fractures, on the other hand, are considered more serious and severe because the bone fragments could be in many pieces and probably moved out of their proper positions. In displaced fractures, the distortion of the injured area is usually very visible and causes extreme bouts of pain.
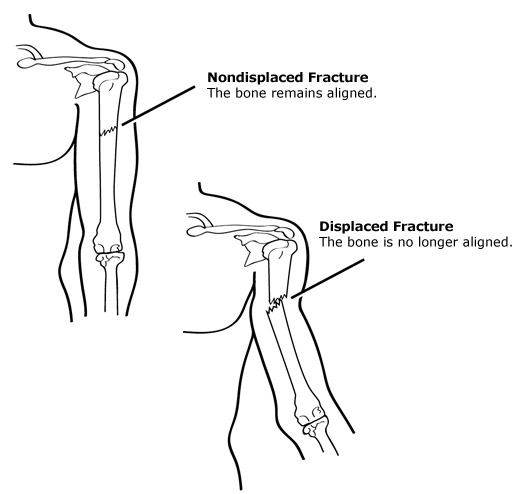
Types of Displaced Fractures
• Open fracture- the fragmented bone pierces the skin, creating a wound.• Closed fracture- the bone is displaced but the skin is kept intact.
• Complete fracture- the bone is fragmented and the broken pieces separate completely from the main body of the bone.
• Comminuted fracture- the fracture case caused the bone to break in several but large fragments.
• Multi-fragmentary fracture- the bone splits into many small pieces.
Diagnosis
Displaced fractures are diagnosed by having the patient undergo a medical evaluation, physical examination, and x-rays. In the medical evaluation, the physician will ask the patient how the accident happened and where the location of the fracture is. The medical history of the patient will also be inquired to identify if the patient has some pathological problems that need to be considered in the treatment.
After this, a physical examination will be conducted to assess the degree of the fracture, the level of displacement of the bone, and if there are any neighboring tissues or surfaces that were affected by the fracture. If the physician thinks that the fracture has affected a joint, an x-ray will be required in order to identify the extent movement of the bone from its normal position. In some cases, normal x-ray scans are not enough to provide a good assessment of the level of displacement. In a case like this, special radiological scans like MRIs and CT scans will be recommended by the doctor.
Displaced Fracture Causes
A displaced fracture is commonly the result of a strong force colliding with the bones. Traumas from accidents and force from heavy physical sports can cause bone displacements. Accidents like jamming on a hard surface, bone forcefully crushed, or bone getting twisted can also cause bone displacements.Displaced Fracture Symptoms
• Tenderness• Pain
• Numbness
• Swelling
• Deformity on the injured area.
• Extreme pain when the affected area is moved.
• Inability to do any normal movements
Displaced Fracture Treatment
The treatment for a displaced fracture will depend on whether the injury is an open or a closed fracture. Open displaced fractures will immediately require surgery because leaving them for too long can cause infections and other complications. In surgery, metal wires, rods, plates, and screws are internally fixed on the bones to join their displaced ends. Some cases make use of bone grafting wherein a healthy part of the bone from another part of the body will be taken and will be implanted on the injured area.For closed fractures, these can be normally treated through external fixation. There are two methods of external fixation. The first one requires the use of simple immobilization tools such as casts and slings to move back the displaced bones on their proper alignment. The other type also makes use of screws and pins but they are not implanted on the body. Instead, a metal ring or band is placed on the injured area and the screws are positioned above and below the frame. The screws are the knobs, which control the adjusting of the metal frame and the frame is the one that keeps the bones aligned.
Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.