The human body is supported by the bones in it that allow movement and protection of the important organs inside. They even help in storing the nutrients that are needed by the body to function well. Thus, you need to take care of your bones in order to let them continue to function the way that they should. These bones are also built and established hard with the help of calcium phosphate. As this mineral is deposited in every bone that you have in your body, this will undoubtedly make you and your bones stronger.
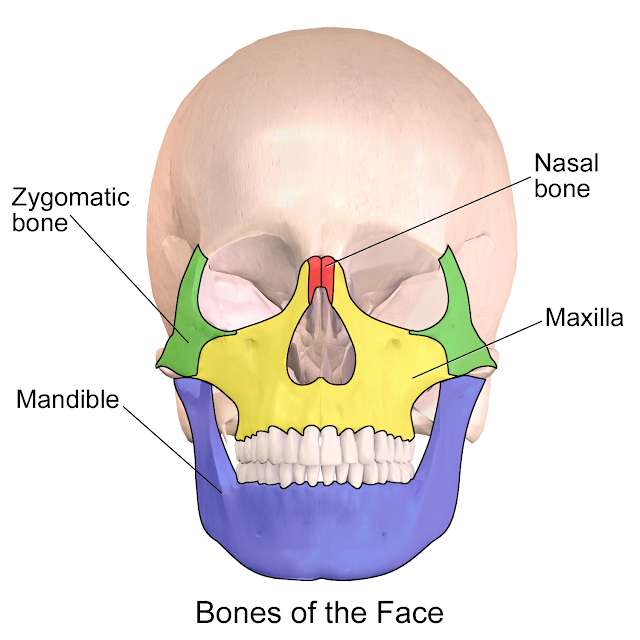
Anatomy
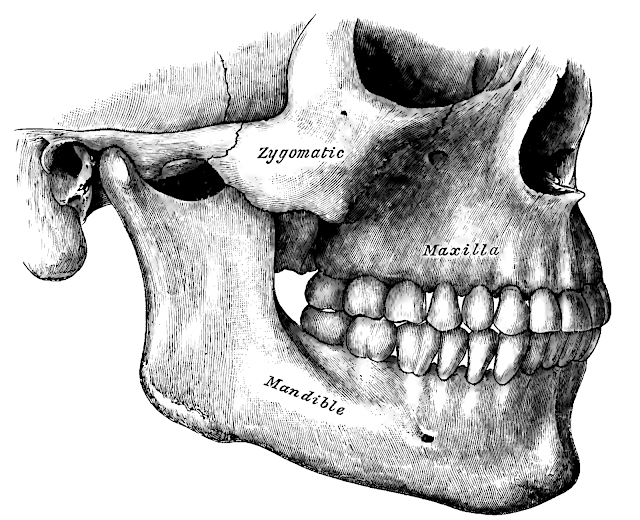
A zygomatic bone is one of the bones in the body, particularly found on the upper and lateral portion of the face. It is the type of facial bone that gives the form to the cheek. A zygomatic bone composes the infratemporal and temporal fossae, forming the floor of the orbit and a part of the lateral wall near the cheek. Like many other bones in the body, this is also at risk of being broken or fractured. A fractured zygomatic bone can happen when the face gets a substantial blow during a clench hand battle or mishap. In boxing, there are examples when the clench hand of the adversary will land right deep down close to your cheeks, where this facial bone is. Therefore, a boxing call can open the individual to the dangers of having a zygomatic bone fractured.
Zygomatic Fracture
A zygomatic fracture could affect the orbiting part of the face. This type of fracture of facial bone is usually caused by a blowout fracture. A zygoma fracture affects the orbital floor and/or the medial wall on the face. There are cases when the bone fracture is dislocated or just broken. While the zygoma bone’s central part seems to stay untouched, the strength of the impact would instead be felt by the three buttresses. When any of these three buttresses are affected by the impact, this could result in any of the following conditions:- Intraorbital fracture
- Zygomatic arch fracture
- Displaced zygomatico-frontal structure
Gender Occurrence
While the parents are already looking forward to the fracture healing time wherein the face can be completely used without a hitch, some are still worried about a zygomatic fracture in children. In most cases though, more males are exposed to the risk of zygomatic fractures than do women. This is also the same case with orbital fractures. The risks are higher for people at the age of 10 to 40 and those aged 70 years and above. Thus, facial fractures that occur at the age of 41 to 69 would likely not increase the chances of having to experience some orbital fractures or zygomaticomaxillary complex. This is also noted as a ZMC fracture.
- Symptomatic enophthalmos of less than 2mm
- Damage of more than 50% on the orbital floor
- Failure of the diplopia to get cured after two to three weeks.
These are all the basic things that patients should be aware of if one has zygomatic bone fractures. This way, there would be no mistake that would cause the patient even more pain and agony. There are certain things that can only make the fractured bone even more damaged.
Zygomatic Arch Fractures
Among all the facial bones, the nasal bone is the most injury-prone zygomatic bone. The incidence of exposure to zygoma fractures ranks second with the zygoma. Young males are the usual victims of this type of fracture injury too. This could be due to the fact that they are also the ones who are typically involved with trouble that leads to injury on the face. The trauma to the zygomatic arch is usually caused by vehicular accidents, assault and sometimes, contact sports.Future Assessment
The patient will usually be asked about the following things:- Numbed area. The upper lip or infraorbital part of the face would likely feel numbed. This numbness could also spread to the canine teeth, central teeth, or lateral teeth. These are teeth that are found near the maxillary part of the face. This is why the ZMC fracture also happens. This can be felt among 70 to 90 percent of the patients with injured zygomatic parts of their faces.
- Injury mechanism. The doctor will ask the patient about the incident that led to the zygoma fracture. This allows the doctor to examine if there might be foreign objects inside some open wounds, especially in open zygomatic fractures.
- Zygomatic fracture symptoms. Some visual symptoms would include a hematoma or neural injury.
- Other fracture symptoms. These include pain during the spasm of the masseter. This movement is also called trismus. Retrobulbar hemorrhage is signaled by severe pain with visual loss at tines.

Zygomatic Fracture Diagnosis
After asking the patient about one’s medical history and after the physical examination, the diagnosis should be done to determine if one has a fracture on the zygomatic arches.- X-ray of the skull. This is the most basic diagnostic test that lets the doctor see the facial, submento-vertical and occiptomental. The doctor can then check all the results to know how to heal the fracture. This diagnosis is also done for sternum fracture, in as much as it is necessary for calcaneus fracture. To give an estimate of the recovery time for an injury like or even for mandible fracture maxillary fracture, a well-done diagnosis should also be performed.
- CT scan. This is a more advanced type of diagnosis to examine the anatomy of the patient’s facial make up. This is necessary if the doctor sees to it that fracture surgery might be necessary to know how to treat zygomatic fracture quick. In some cases, medicines have to be taken to ease the pain away. Emedicine can be obtained online for the convenience of the patients. By CT scanning, some displaced fractures can be seen as well.
- Ultrasound. This is necessary for getting an image of the butterfly fracture. The images would also be necessary for assessing the zygomatic complex fracture. These images can help the doctor clearly see as to how to treat the zygomatic fracture.
- MRI scan. This is inferior to a CT scan, but this is still useful in detecting soft tissue herniation. Moreover, this helps determine the presence of metallic foreign bodies inside the patient’s body if there is an open wound in the zygomatic injury.
Management of the Fractured Zymgomatic Bone
- The nose should not be used for blowing within the next ten days after the accident.
- The patient might need to consult with maxillofacial surgeons and ophthalmologists.
- Some zygomatic fracture treatment would entail the use of antibiotics along with outpatient monitoring.
- Surgery as the zygomatic fracture treatment is necessary in cases like:
- Symptomatic enophthalmos of less than 2mm
- Damage of more than 50% on the orbital floor
- Failure of the diplopia to get cured after two to three weeks.
Zygomatic Fracture Complications
Some complications that should be watched out for are optic nerve damage, globe injury, and persistent diplopia, which will only delay the surgery even more. If the patient has a zygomatic tripod fracture, the case should be handled with more care.Prevention of Zygomatic Fracture
Fractures are usually experienced by people during accidents. There are some tips to help prevent accidents and bad impacts on one’s life.- Always wear seatbelts to help avoid injuries during road traffic and vehicular accidents. A Brazilian study tried to cover the relationship between the wearing of seatbelts and types of facial fractures. With the seatbelt on, further injuries and fractures can be prevented.
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol. A drunken person can easily find trouble, which prompted some people to promote the use of anything plastic in a place where drinking is allowed. When brawling ensues, the troublemakers might wake up the next day with broken zygomatic bones. Other recommendations would even attempt to touch the pricing and distribution of alcohol to people. The bad news is that you might have limited facial actions while waiting for the zygomatic fracture healing time to be over.
- Use protective equipment during a contact sports game. However, even with the protective gears on, the fracture of zygoma might still not be prevented. There are cases when head butts would be the reason for the tear or fracture on the face of the patient due to the impact of the heads banging together.
These are all the basic things that patients should be aware of if one has zygomatic bone fractures. This way, there would be no mistake that would cause the patient even more pain and agony. There are certain things that can only make the fractured bone even more damaged.
Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.