The ulna is one of the main bones found in the forearm together with the radius. Isolated ulna fractures commonly happen when the forearm received a direct blow like a hit from a hard object. Based from hospital records, men are more prone to ulna fractures than women because of their tendency to participate in sports and strenuous activities, which can cause damage to the forearm bones. Also known as nightstick fractures, these injuries can happen on the subcutaneous border of the ulna bone.
Types of Ulna Fractures
Ulna bone injuries can also be termed as stress fractures or Monteggia fractures.
• Ulna Stress Fractures are the result of repetitive stress on the ulna bone creating hairline cracks, which can worsen into fractures when not immediately treated.
• Monteggia Fractures are due to injuries on the proximal part of the ulna bone which are commonly connected with the bone of the radial head and suffer dislocation.
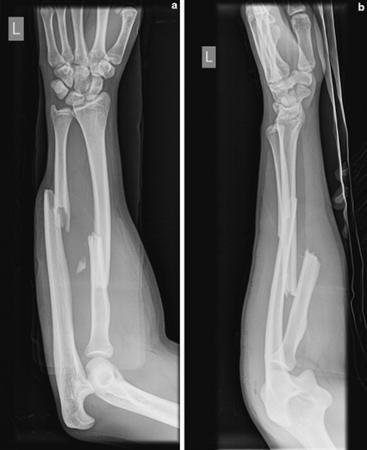
Diagnosis
In diagnosing ulna injuries, a physical examination is done first. Here, the doctor will examine the affected limb for any signs of deformity, breakdown, hematoma formation, or discoloration. Palpation or gentle pressure will be applied on the forearm and the wrist to see if the patient suffers from sore and tenderness. Afterwards, neurological and vascular examination using the 2-point discrimination procedure will be conducted in order to remove the possible cases of concomitant injuries on the neurovascular parts. The muscle and tendon functions will also be tested by the doctors by asking the patient to do a couple of wrist and fingers range of motion exercises. As for the tests, the lateral, oblique, and standard AP radiographs of the forearm and elbow can be requested by the doctors. The radiograph of the forearm should also include a scan of the wrist. In analyzing these shots, radiographic lines are used by the physician to evaluate the extent of the injury.
Causes
An ulna bone fracture can either be caused by a sporting accident or application of repetitive stress on the ulna area or the forearm. People who participate in wrestling, football, and other rough sports are the ones most at risk in having this type of bone injury. Individuals who also constantly put too much strain on their limbs and arms either because of work or training are also very likely to get ulnar fracture. In other cases, a person gets a fractured ulna because of calcium deficiency which makes the bones fragile.
Symptoms
• Pain and swelling on the forearm
• Arm deformity on the specific broken area
• Limited arm movement of the whole arm
• Tenderness on the injured area
Ulna Fracture Treatment, Healing and Recovery:
For cases of minimally displaced or non-displaced ulna fractures, the basic treatment prescribed is the use of a sugar-tong splint. This should be worn by the patient for approximately 7-10 days. After this, the individual will wear functional bracing for not more than 8 weeks. This is supplemented by physical therapy like motion exercises of the wrist, hand, and elbow. Based from the symptoms the patient exhibits, the use of sling that is equipped with a compression wrap can also be recommended. As for displaced fractured ulna and radius fracture, they are normally treated by using internal fixation and open reduction.
Monteggia fractures, moreover, are often treated through surgery. Since the radial head is affected here, surgery must be performed with the patient under a general anesthesia. This will be followed by internal fixation and open reduction of the ulna bone shaft by using a dynamic compression plate. Most of the times, internal fixation can solve the problem of the dislocation of the radial head. However, in cases when internal fixation still cannot stabilize the ulna, implanting a radial nerve can be an option. After the operation, the patient is required to wear a splint supporting his posterior elbow for a week. Once the splint is not needed, physical therapy of the forearm and elbow with exercises should be done.
Prevention of distal radius and ulna fracture:
The use of protective gears while participating in sports or in doing work that requires major use of the limbs can help a lot. For those who have ulnar fractures, the best prevention is taking it easy on the stress that will be applied to the limbs and arms. Having calcium supplements can also help a lot in strengthening the bones.
When to Call a Doctor
An individual who had an accident and injured arm should immediately go to the doctor regardless if he is experiencing pain or not. People who also constantly put stress on their limbs and experience sudden pains on their arms should likewise drop by their physicians’ office because the pains may be caused by stress fractures.
Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.